What is an Endangered Plant?
What is an Endangered Plant?
What is an endangered plant?
Endangered plants are defined to be vulnerable to become extinct in the near future. In Japan, the endangered plants at national level are designated by the Ministry of Environment, and those at regional level are designated by each regional government.
Endangered plants are classified into seven categories according to how they are threatened to extinct in Japan. Criteria.
Endangered Species Categories and Definitions
| Category | Definition |
| Extinct (EX) | no reasonable doubt that the last individual has died |
| Extinct in the Wild (EW) | extinct in its natural habitat |
| Critically Endangered (CR) | Extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. |
| Endangered (EN) | High risk of extinction in the wild. |
| Vulnerable (VU) | High risk of endangerment in the wild. |
| Near Threatened (NT) | Likely to become endangered in the near future. |
| Data Deficient (DD) | Not enough data to make an assessment of its risk of extinction. |
※ *For detailed information, seeIUCN (2016) Guidelines for Uisng the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria
Red Data Books
 Red Data Books published nationally (Ministry of the Environment, 2000) and by prefectural governments
Red Data Books published nationally (Ministry of the Environment, 2000) and by prefectural governments
Current Situation in Japan
Endangered Plant Species in Japan
Approximately 7,000 plant species grow naturally on the Japanese archipelago, of which about 2,900 species (roughly 40%) are endemic to Japan. Japan has a very high species density and a large proportion of endemic plants by global standards, making its plant life an important biological resource.
Unfortunately, out of these 7,000 species, 1,690 are classified as endangered plants (narrower category), meaning that one in every four valuable native Japanese plant species is at risk of extinction.
| Category | 2007 (Latest) | 2000 (Previous) | Change |
| Extinct (EX) | 33 | 20 | 13 |
| Extinct in the Wild (EW) | 8 | 5 | 3 |
| Critically Endangered (CR) *Endangered Plants (Narrower Category) |
523 | 564 | -41 |
| Endangered (EN) *Endangered Plants (Narrower Category) |
491 | 480 | 11 |
| Vulnerable (VU) *Endangered Plants (Narrower Category) |
676 | 621 | 55 |
| Near Threatened (NT) | 255 | 145 | 110 |
| Data Deficient (DD) | 32 | 52 | -20 |
| Total | 2,018 | 1,887 | 131 |
 Wildly Extinct Species: Eriocaulon heleocharioides Satake (Eriocaulaceae)
Wildly Extinct Species: Eriocaulon heleocharioides Satake (Eriocaulaceae)
 Wildly Extinct Species: Dryopteris shibipedis Sa.Kurata (Dryopteridaceae)
Wildly Extinct Species: Dryopteris shibipedis Sa.Kurata (Dryopteridaceae)
Why are they endangered?
Among the factors driving plant extinction in Japan, human activity accounts for about 80%. In particular, deforestation and the collection of plants for horticultural cultivation or trade are major contributing factors. In addition, many natural changes caused by global warming are indirectly linked to human activities. Next, we will explain the main causes.
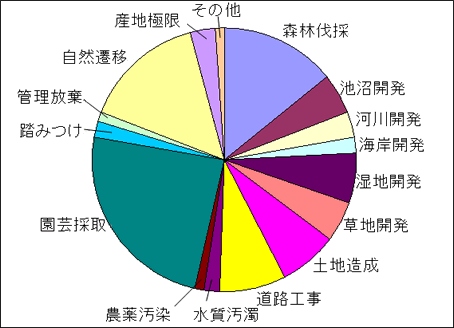 Factors Affecting Endangered Plants (Red Data Book, Ministry of the Environment, 2000)
Factors Affecting Endangered Plants (Red Data Book, Ministry of the Environment, 2000)
Destruction of Natural Habitats
In Southeast Asia, large-scale deforestation is still taking place. The massive amounts of carbon dioxide released by human activities contribute to global warming. This destruction of natural environments has led to the loss of habitats for valuable plant species. Current environmental conservation efforts, often featured on television, are aimed primarily at protecting biodiversity.


Example: The original tropical rainforest has been converted into pastureland.(Veracruz, Mexico)
Rare Plants
Some plants grow naturally in only a single location on Earth and have very small populations. These plants are often adapted to highly specific environments, and even minor environmental changes can lead to their extinction. In such cases, it is necessary to conserve not only the plants themselves but also their surrounding environment.
 Example: Solanum miyakojimense (Solanum), found only on Irabu Island in the Ryukyu Islands.
Example: Solanum miyakojimense (Solanum), found only on Irabu Island in the Ryukyu Islands.
Overharvesting
Among the factors contributing to the increase in endangered plants, habitat destruction is closely linked to human activities and is a very complex issue. However, illegal overharvesting for purposes such as horticultural trade is nothing more than the selfishness of a very small number of people. Because of this overharvesting, many plants are driven to the brink of extinction.
 Example: Endangered cycad with horticultural value, Macrozamia mountperiensis (Australia).
Example: Endangered cycad with horticultural value, Macrozamia mountperiensis (Australia).
 Traces of Overharvesting
Traces of Overharvesting
Plant Damage by Animals
In recent years, damage caused by animals feeding on plants has pushed many species toward extinction and has become a serious problem. In Kyushu, the increase in deer has caused severe damage, leading to a drastic reduction of understory plants. The increase in deer populations is believed to result from disruptions in the ecosystem.
On islands such as Uotsurijima in the Senkaku Islands, goats introduced as livestock and now living in the wild have caused significant damage to many plants. However, we must not forget that humans are responsible for introducing these livestock.
 Examples: Severe overbrowsing by deer in Kirishima.
Examples: Severe overbrowsing by deer in Kirishima.
 Valuable plants damaged by grazing goats.
Valuable plants damaged by grazing goats.