What Is Biodiversity?
What Is Biodiversity?
It represents the "richness of life" on Earth.
Biodiversity is the unique and irreplaceable treasure of Earth, encompassing the vast number of species that have arisen over more than three billion years of biological evolution, the genes carried by each species, and the ecosystems created by various species under diverse environmental conditions, most of which remain largely unknown.
Biodiversity Pie Chart
Currently, there are approximately 2.1 million known species living on Earth, and humans are one of them. It is estimated that there are 10 to 100 times more species than those currently known. Each species varies not only in form and traits but also in its habitat. Biodiversity is the result of more than four billion years of life on Earth, during which species have gone extinct while new ones have continually emerged.
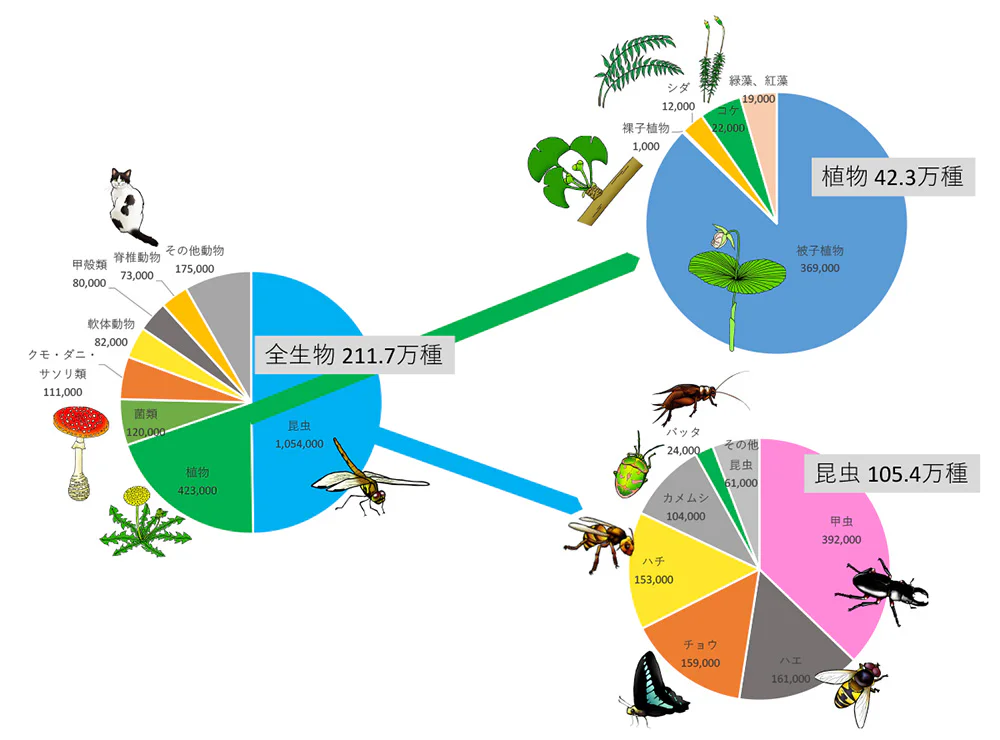 References:
References: IUCN RedList 2021
Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life, 2019 Annual Checklist.
Illustrations by: Aki Hatomi, Yoko Fukumoto
Our Research on Biodiversity
- Creation of Biodiversity Maps for Biodiversity Analysis
- Integration of Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis and Taxonomy
The Role of Plants in the Biological World
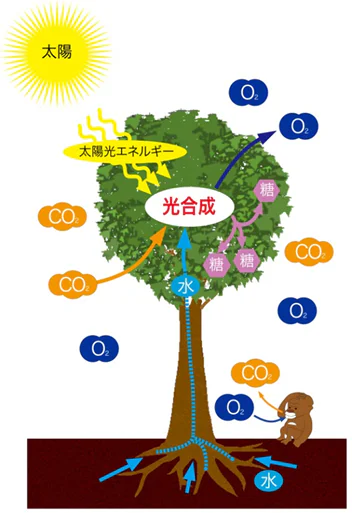
Plants are essential for all living organisms, including humans, because they produce organics from inorganics. Plants also absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and then release oxygen into the air through photosynthesis. Therefore, plants play an important role in the survival of other organisms.
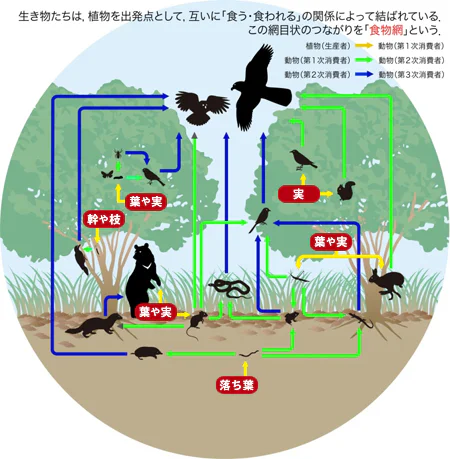
The food web connecting living things
The Mechanism of Photosynthesis
Why Biodiversity Matters
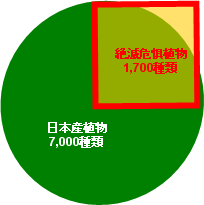
Biodiversity is being rapidly lost due to human activities, and the current rate of extinction is said to be comparable to past mass extinction events. In Japan, one-quarter of wild plant species (1,700 out of 7,000) are at risk of extinction. We investigate the causes of this decline while conserving endangered plants in the garden and presenting them in our exhibits.
Endangered Plant Symbol
Endangered plants researched and conserved by the botanical garden
 Lysionotus apicidens (Hance) T.Yamaz.(Gesneriacea)
Lysionotus apicidens (Hance) T.Yamaz.(Gesneriacea)
 Eriocaulon heleocharioides Satake(Eriocaulaceae)
Eriocaulon heleocharioides Satake(Eriocaulaceae)
 Dryopteris shibipedis Sa.Kurata(Dryopteridaceae)
Dryopteris shibipedis Sa.Kurata(Dryopteridaceae)
 Pieris koidzumiana Ohwi(Ericaceae)
Pieris koidzumiana Ohwi(Ericaceae)
 Liparis truncata F.Maek. ex T.Hashim.(Orchidaceae)
Liparis truncata F.Maek. ex T.Hashim.(Orchidaceae)
 Tricyrtis macranthopsis (Liliaceae)
Tricyrtis macranthopsis (Liliaceae)
 Potamogeton dentatus(
Potamogeton dentatus(Potamogetonaceae)
The Importance of Plants
Plants are connected to other organisms not only through food webs but also through various ecological relationships such as symbiosis and parasitism. If one plant becomes extinct, other related organisms are affected in succession. Just as “a single
ant hole can cause a dam to collapse
(*A small leak will sink a great ship.),” even the extinction of a single plant species can threaten the survival of many organisms. Plants are not only a vital element of the natural environment but also a biological resource. We have utilized over 10%
of all plant species and numerous cultivars in every aspect of our lives. Even plants not currently used today hold the potential to be utilized in some form in the future. Preserving biodiversity is essential for ensuring the next generation can live
prosperous lives.
Plants We Use and Their Purposes
| Food | Medicinal | Ornamental
| Sculptural |
|
|
|
|
In addition, it is utilized for various purposes such as energy.
References The Useful Plants of the World
Examples of useful plants found within the Botanical Garden
 Cacao (Chocolate and cocoa)
Cacao (Chocolate and cocoa)
 toquilla paim(Hats and clothing)
toquilla paim(Hats and clothing)
 Pepper plant(Spices)
Pepper plant(Spices)
 Coffee plant(Beverages)
Coffee plant(Beverages)
 Chestnut(Food)
Chestnut(Food)
 Tea plant(Beverages)
Tea plant(Beverages)
 Tea plant(Beverages)
Tea plant(Beverages)
Photo courtesy of Kinue Sato